"Polymorphism" is a greek word, "poly" means many and "morph" means forms.
In object oriented programming paradigm Polymorphism is expressed as one object behaving as multiple forms. One function behave in different forms.
Sharing my knowledge, experience using this Blog on various Microsoft Technologies like WPF, C#, XAML, LINQ, WCF, ASP.Net, And database like SQL Server, Oracle And ORM technologies like NHibernate.
Tuesday, 28 February 2017
Polymorphism in OOP
Inheritance in OOP
Inheritance
One of the most important concepts of object oriented programming is Inheritance. Inheritance is a mechanism of acquiring features and behaviors of one class called as base or parent class into another class called as derived class.
Inheritance implements a IS-A relationship.
Advantages of inheritance
- Code re-usability
- Reduction in code size
- Improve code readability
- Code extensible support by overriding base class method into derived class
Disadvantage of inheritance
- Tight coupling between base class and child class
- Performance of your program is affected if inheritance is not implemented properly.
- Many unused data members remain unused & memory is allocated for the same.
Different types of inheritance
- Single Inheritance
When a derived class is created from a single base class.
C# Example
public class Parent
{//Definition}
public class Derived : Parent{//Definition}
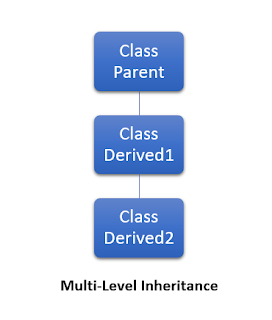
- Multi-Level Inheritance
When a derived class is created from another derived class is called as multi-level inheritance
C# Example
ppublic class Parent
{//Definition}
public class Derived1 : Parent{//Definition}
public class Derived2 : Derived1{//Definition}
- Multiple Inheritance
When a derived class is created from more than one class then it is called as multiple inheritance. This type of inheritance is not supported in C# or .Net
This type of inheritance is not supported in C# or .Net
- Hierarchical Inheritance
When a multiple derived class is created from one single class then it is called as Hierarchical inheritance.
C# Example
public class Parent{//Definition}
public class Derived1 : Parent{//Definition}
public class Derived2 : Parent{//Definition}
public class Derived3 : Derived1{//Definition}
public class Derived4 : Derived1{//Definition}
public class Derived5 : Derived2{//Definition}
public class Derived6 : Derived2{//Definition}
- Hybrid Inheritance
This is combination of more than one inheritance. It may be a combination of Multilevel and Multiple inheritance or Hierarchical and Multilevel inheritance or
Hierarchical and Multilevel and Multiple inheritance.
- Why C# does not support multiple inheritance?
C# does not support multiple inheritance because of diamond problem. To know more about diamond problem please refer below link
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiple_inheritance#The_diamond_problem
- As we know multiple inheritance is not supported by C# or .Net what is the other way to achieve multiple inheritance in C# or .Net?
We can achieve similar functionality using interface in C#.
- Is static class can be inherited ?
Static class can not be inherited. C# complies static class as sealed abstract class hence static class cannot be inherited in c#.
- How to make normal class non inheritable c#?
Using sealed keyword in c# we can stop class from further inheriting it.
Thursday, 24 July 2014
Export to CSV from a List of class object(s).
Export to CSV from a List of class object(s).
Today I got an assignment to transfer/export data into CSV file from a
List of class object so I thought to make it generic so that I can use it in
multiple modules and projects too, but how with the following challenges?
Exclude Class Property.
Custom Header.
No Header.
Column Order while exporting to CSV.
Should be Generic.
The solution came to mind is to use C# Attribute to handle the challenges.
Attribute (MSDN):Attributes provide a powerful
method of associating metadata, or declarative information, with code
(assemblies, types, methods, properties, and so forth).
Reflection (MSDN): Reflection provides objects (of
type Type) that describe assemblies, modules and types. You can use reflection
to dynamically create an instance of a type, bind the type to an existing
object, or get the type from an existing object and invoke its methods or
access its fields and properties. If you are using attributes in your code,
reflection enables you to access them. Using reflection I can extract the property
information or custom attribute provided for CSV.
Generics (MSDN):Generics introduce to the .NET
Framework the concept of type parameters, which make it possible to design
classes and methods that defer the specification of one or more types until the
class or method is declared and instantiated by client code.Generics used to
export any List of class object without re-writing code again and again.
Let’s start with designing Attribute.
using System;
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Property, AllowMultiple = false, Inherited = false)] public class CSVAttribute : Attribute { private readonly bool allowExport; private readonly int order; private readonly string columnHeader; private readonly string format; public CSVAttribute(bool allowExport = false, int order = 0,
string columnHeader = "") { this.allowExport = allowExport; this.order = order; this.columnHeader = columnHeader; } public CSVAttribute(bool allowExport = false, string columnHeader = "",
int order = 0, string format = "") { this.allowExport = allowExport; this.order = order; this.columnHeader = columnHeader; this.format = format; } public string ColumnHeader { get { return columnHeader; } } public bool AllowExport { get { return allowExport; } } public int Order { get { return order; } } public string Format { get { return format; } } }
So we have defined CSVAttribute which will be applied at property level,
multiple definitions on same property is not allowed and it is not inherited.
This attribute has constructor which take three values
1. AllowExport (whether you want to export to CSV default is false).
2. ColumnHeader (Column Header you want to write while exporting).
3. Order (Order in which you want column to be printed).
1. AllowExport (whether you want to export to CSV default is false).
2. ColumnHeader (Column Header you want to write while exporting).
3. Order (Order in which you want column to be printed).
Let’s now define the Custom CSVPropertyInfo Class which we will use
during export to CSV option.
using System.Reflection; public class CSVPropertyInfo { public PropertyInfo Property { get; set; } public CSVAttribute Attribute { get; set; } }
Now time to define the CSVFileWriter
class who is responsible for writing the header and data in CSV for provided
property or propertied only.
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Reflection; using System.Text;
public class CSVFileWriter<T> : ICSVFileWriter<T> where T : class { private List<T> Data { get; set; } private IEnumerable<CSVPropertyInfo> ExportProperties { get; set; } private string Headers { get { var headerName = new StringBuilder(); foreach (CSVPropertyInfo property in ExportProperties) { headerName.Append(string.Format("\"{0}\",",
property.Attribute.ColumnHeader)); } headerName.Remove(headerName.Length - 1, 1); return headerName.ToString(); } } public void Write(string fullFileName, List<T> data, bool writeHeader = true) { if (data == null || !data.Any()) { throw new Exception("Please provide the data"); } Data = data; SetExportProperties(); var fileData = new StringBuilder(); if (writeHeader) { fileData.AppendLine(Headers); } fileData.Append(GetRowData()); WriteFile(fullFileName, fileData.ToString()); } private void SetExportProperties() { var properties = new List<CSVPropertyInfo>(); foreach (PropertyInfo property in Data.First().GetType().GetProperties()) { object[] attrs = property.GetCustomAttributes(true); foreach (CSVAttribute attr in attrs
.Where(x => x.GetType() == typeof(CSVAttribute))) { if (attr != null && attr.AllowExport) { properties.Add(new CSVPropertyInfo {
Attribute = attr,
Property = property }); } } } ExportProperties = properties.OrderBy(x => x.Attribute.Order).ToList(); } private string GetRowData() { var sb = new StringBuilder(); foreach (T data in Data) { var row = new StringBuilder(); foreach (var property in ExportProperties) { if (property.Attribute.Format.Length > 0) { var propType = property.Property.PropertyType; if (propType == typeof(DateTime)) { row.Append(string.Format("\"{0}\",",
Convert.ToDateTime(property.Property.GetValue(data, null))
.ToString(property.Attribute.Format))); } else if (propType == typeof(double) || propType == typeof(float)) { row.Append(string.Format("\"{0}\",",
Convert.ToDouble(property.Property.GetValue(data, null))
.ToString(property.Attribute.Format))); } else { row.Append(string.Format("\"{0}\",",
Convert.ToDouble(property.Property.GetValue(data, null)))); } } else { row.Append(string.Format("\"{0}\",",
Convert.ToString(property.Property.GetValue(data, null)))); } } row.Remove(row.Length - 1, 1); sb.AppendLine(row.ToString()); } return sb.ToString(); } private void WriteFile(string fullFileName, string data) { using (var streamWriter = new StreamWriter(fullFileName, false)) { streamWriter.Write(data); streamWriter.Close(); } } } public interface ICSVFileWriter<T> where T : class { void Write(string fullFileName, List<T> data, bool writeHeader = true); }
So our CSV writer is ready now to get export we need to implement
attribute in our class.
For example we have Employee class as follow.
publicclassEmployee
{
[CSV(true, "Date of Birth", 3)]
publicDateTime DOB { get; set;
}
[CSV(true, "First Name",1)]
publicstringFirstName { get; set; }
[CSV(true, "Last Name", 2)]
publicstringLastName { get; set; }
publicstringUserId { get; set; }
}
Once the attributeis defines it is ready for export. In above class we
have not places CSV attribute on UserId so this field will not be
considered while exporting data. The order for column we have defined which is
different than the property order in class. The Second parameter in CSV is
Column Header for DOB property we will use column Header as a Date of
Birth. Now let’s execute the actual export.
varemployeeList = newList<Employee>
{
newEmployee
{
DOB = DateTime.Now.AddDays(-365*28),
FirstName = "K",
LastName = "P"
},
newEmployee
{
DOB = DateTime.Now.AddDays(-365*28),
FirstName = "P",
LastName = "D"
},
newEmployee
{
DOB = DateTime.Now.AddDays(-365*29),
FirstName = "M",
LastName = "G"
}
};
varcsvFileWriter = newCSVFileWriter<Employee>();
csvFileWriter.Write("c:\\Test\\Employee.csv",
employeeList);
Happy Coding.J
Monday, 2 September 2013
What is MVC?
In
technology world MVC stands for Model View Controller; MVC
is an architectural design pattern to develop the software. MVC design pattern is
widely used to develop a web application.
Model:
Model represents the real life entity such as customer. Model consists of
application data, business rules, logic and functions.
View:
View represents the model data on UI or page (web application). View is actual representation
of data in user friendly format. View present data in terms of user controls, charts,
diagrams etc.
Controller:
Controller is mediator between Model and View. It takes model data and
represents it on the view. It could also take input from the user and send to
the model for further processing or to take action on it by model.
This
design pattern is exists since 1970. The MVC pattern is widely used with
programming languages such as Java, Smalltalk, C, and C++. Now Microsoft Web Developer
can easily integrate this design pattern with Asp.Net application using RAZOR
or ASPX engine.
Now
next question comes into your mind is that why should I use MVC or what are the
advantages of using the MVC design pattern?
Following
are the advantages of using MVC pattern
- Separation of concerns: View is only responsible for displaying data on UI. No business logic is tightly integrated in view. Controller is responsible for processing user requests. Business logic now resides in a model.
- Unit Testing: You can test your business logic using Unit test tools such as NUnit, xUnit etc.
- TDD: TDD stands for Test Driven Development, In TDD approach developer will always writes test first for a module or business logic. This approach is helpful in early detection of an issue in development.
Tuesday, 9 July 2013
Generic Cache Manager
To improve the performance of an application many a times we need to cache frequently used data. This generic cache manager will help to maintain cache using concurrent dictionary (Key, Value Pair). Concurrent Dictionary represents a thread-safe collection of key/value pairs that can be accessed by multiple threads concurrently.
Generic cache manager allows you to add, delete and retrieve data from the concurrent dictionary.
If you are using dependency injection or container like Unity, Windsor-Castle etc. in your application then you have to register cache manager as a Singleton. Otherwise you can achieve a singleton pattern by making CacheManager class and its method as a static. Following is the generic Cache Manager code.
using System;
public interface ICacheManager
{
/// <summary>
/// Add a new object into the cache
/// </summary>
/// <param
name="key">The key of the object
to add</param>
/// <param
name="value">The value of the
object to add</param>
void
Add(string key, object
value);
/// <summary>
/// Check whether the key is contained by the cache
/// </summary>
/// <param
name="key">The key to check</param>
/// <returns>Returns true if the key is contained by the cache</returns>
bool
Contains(string key);
/// <summary>
/// Returns the number of items in the cache
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
int
Count();
/// <summary>
/// Get the object that its key is given
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam
name="T">The object</typeparam>
/// <param
name="key">The given key to check</param>
/// <returns>returns the object or null if it doesn't exists</returns>
T Get<T>(string
key);
/// <summary>
/// Get the object that its key is given
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam
name="T">The object</typeparam>
/// <param
name="key">The given key to check</param>
/// <param
name="getData">Function that
retrieves the data </param>
/// <returns>returns the object or null if it doesn't exists</returns>
T SafeGet<T>(string key, Func<T>
getData);
/// <summary>
/// Removes the object that is referenced by the given key
/// </summary>
/// <param
name="key">The given key</param>
bool
Remove(string key);
}
using System;
using
System.Collections.Concurrent;
public class CacheManager
: ICacheManager
{
private
readonly ConcurrentDictionary<string, object>
cache;
public
CacheManager()
{
cache = new
ConcurrentDictionary<string, object>();
}
public void Add(string key, object value)
{
cache.AddOrUpdate(key, value,
(newKey, newValue) => value);
}
public bool Contains(string
key)
{
return
cache.ContainsKey(key);
}
public int Count()
{
return
cache.Count;
}
public
T Get<T>(string key)
{
return
cache.ContainsKey(key) ? (T) cache[key] : default(T);
}
public
T SafeGet<T>(string key, Func<T> getData)
{
return
(T) cache.GetOrAdd(key, x => getData());
}
public bool Remove(string
key)
{
object
output;
return
cache.TryRemove(key, out output);
}
}
Example:
How to add objects or data into the cache.
cacheManager.Add(<<key>>, <<data>>);
How to get data from the cache.
var cacheData = _cacheManager.Get<T>(<<key>>);
Wednesday, 8 May 2013
What is Action,Func delegate in C#
Action:
Encapsulates a method that has no parameter or one parameter or more parameters and does not return a value, method return type should be void(c#) or Sub .... End Sub (vb.net).
E.g.
class Program
{
Encapsulates a method that has no parameter or one parameter or more parameters and does not return a value, method return type should be void(c#) or Sub .... End Sub (vb.net).
E.g.
class Program
{
static void Main(string[]
args)
{
Action<int> action = new
Action<int>(DoSomething);
action.Invoke(1009);
}
static void DoSomething(int
i)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
}
O/P:
1009
Func:
Encapsulates a method that has no parameters or one or parameters and returns a value of the type specified by the TResult parameter.
//Func delegate with one parameter and TResult
public delegate TResult Func<in T, out TResult>(T arg)
E.g.
class Program
{
private
static void
Main(string[] args)
{
Func<int, double>
func = new Func<int, double>(CalcualteSomething);
Console.WriteLine(func(5));
//Should Print 25
}
private
static double
CalcualteSomething(int i)
{
return
(double) i*2;
}
}
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Custome Service Class to connect wcf service
using System; using System.ServiceModel; namespace Custom.Service.Client { // Borrowed from: http://old.iserviceoriented.com/blog/p...
-
As per standard development process we are hosting application after new Iteration (Aglie Methodology) or module development. For client t...
-
The Major components of WPF Architecture are Presentation Framework, Presentation Core and Media Integration Layer. The architecture divid...
-
using System; using System.ServiceModel; namespace Custom.Service.Client { // Borrowed from: http://old.iserviceoriented.com/blog/p...